Email Forensics with Belkasoft X
Email (or mailbox) forensics involves acquiring and analyzing data from email accounts and related systems to gather evidence for legal or investigative purposes. Forensic analysis of emails can reveal a person's communication patterns and other online interactions, such as purchases, service subscriptions, and social media activity.
Another crucial aspect of email forensics is detecting the origin of a cyberattack. By analyzing email metadata, content, and attachments, investigators can identify suspicious activities, phishing attempts, malicious content, and potential indicators of compromise (IOCs).
In this article, we will discuss the main points of interest and essential techniques for email forensic analysis:
- Key steps in mailbox forensics
- Extraction of email data
- Metadata and content analysis
- Attachment analysis
- Email data analysis techniques
- Reporting on and exporting email evidence
We will explore the challenges that may arise along the way and demonstrate Belkasoft X’s features that can help get the most out of email data for your investigations.
Key steps in mailbox forensics
Email forensics involves extracting and analyzing data from email clients, servers, or backup files to identify evidence. In general, this workflow can be divided into several key steps:
- Extraction of data: Parsing email contents and reconstructing folder structures from various data storage formats
- Metadata and content analysis: Examining email headers and content to detect signs of fraud, phishing attempts, or tampering.
- Attachment inspection: Analyzing attached files, such as documents, images, audio files, and executables, to identify malicious content or critical evidence.
- Data correlation and pattern recognition: Linking data to uncover communication patterns or hidden relationships.
- Reporting and exporting: Reporting on discovered evidence and exporting the files.
Digital forensics tools like Belkasoft X streamline these tasks by processing mailbox source files, presenting their contents in a user-friendly interface, and offering analytical tools to enhance your investigations.
Extraction of email data
Email applications store data on computers in a variety of formats and mostly use SQLite on mobile devices. Belkasoft X extracts emails, together with their metadata and attachments from a wide range of email storage formats, ensuring compatibility with commonly used clients such as:
- Microsoft Outlook PST and OST files
- Mozilla Thunderbird MBOX files
- Apple Mail databases
- TheBat! email archives
- Standalone EML or MSG files and more
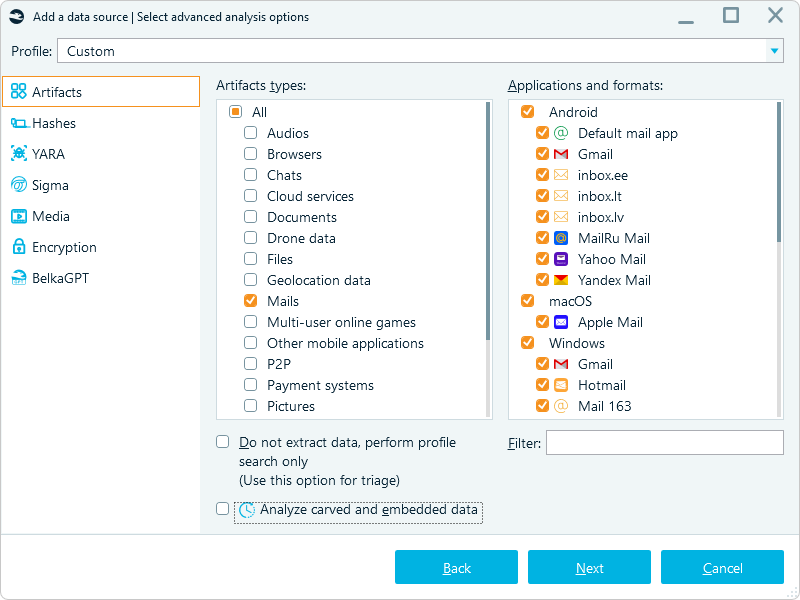
Belkasoft X email data analysis options
When extracting and analyzing email data, Belkasoft X recreates the mailbox folder structure in the artifact tree view:
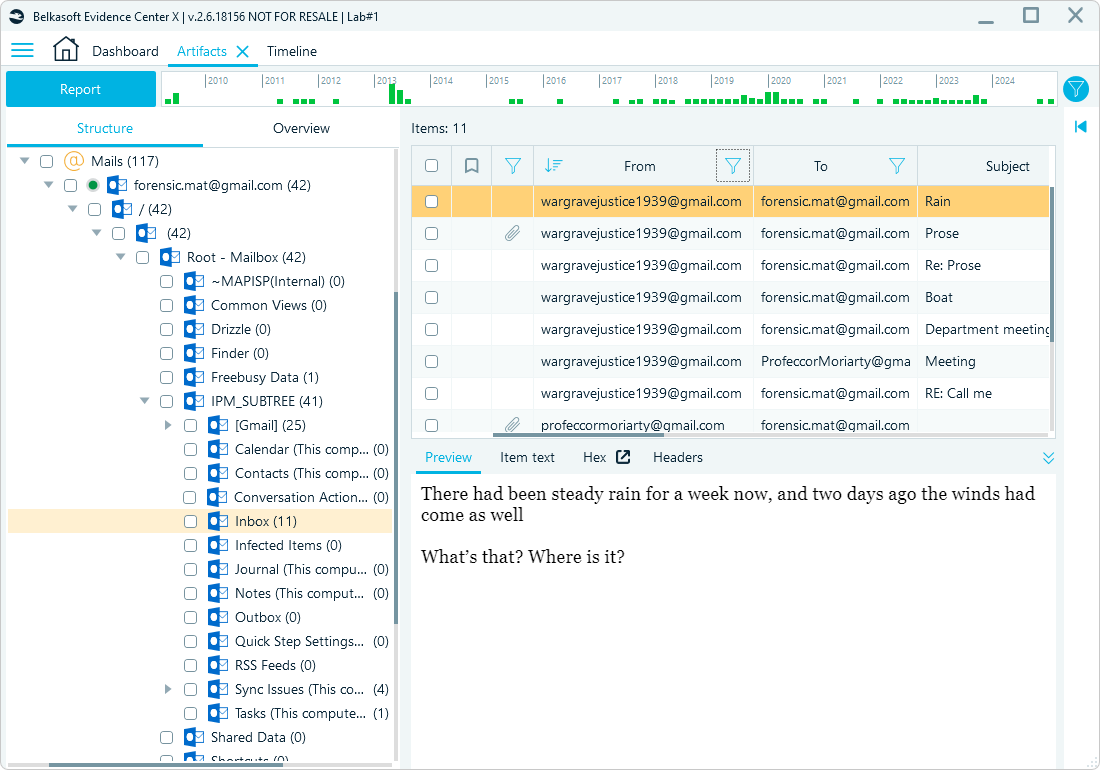
An Outlook email folder structure in Belkasoft X
By structuring email data this way, Belkasoft X makes it easy to review, filter, and analyze mailboxes, ensuring efficient and accurate email investigations.
Metadata and content analysis
Email headers contain details about each message, such as sender and recipient information, routing paths, timestamps, and authentication results. The content of emails can help detect phishing attempts and signs of fraudulent activities or malicious intent.
In this section, we will explore the main aspects of email metadata and content analysis, providing practical tips to help your investigative process.
Filtering emails
Belkasoft X parses data from email headers, allowing you to filter messages by key fields such as From, To, Subject, and Date. It helps you quickly identify potentially suspicious emails based on unusual senders, subjects, or irregular timestamps that deviate from typical communication patterns.
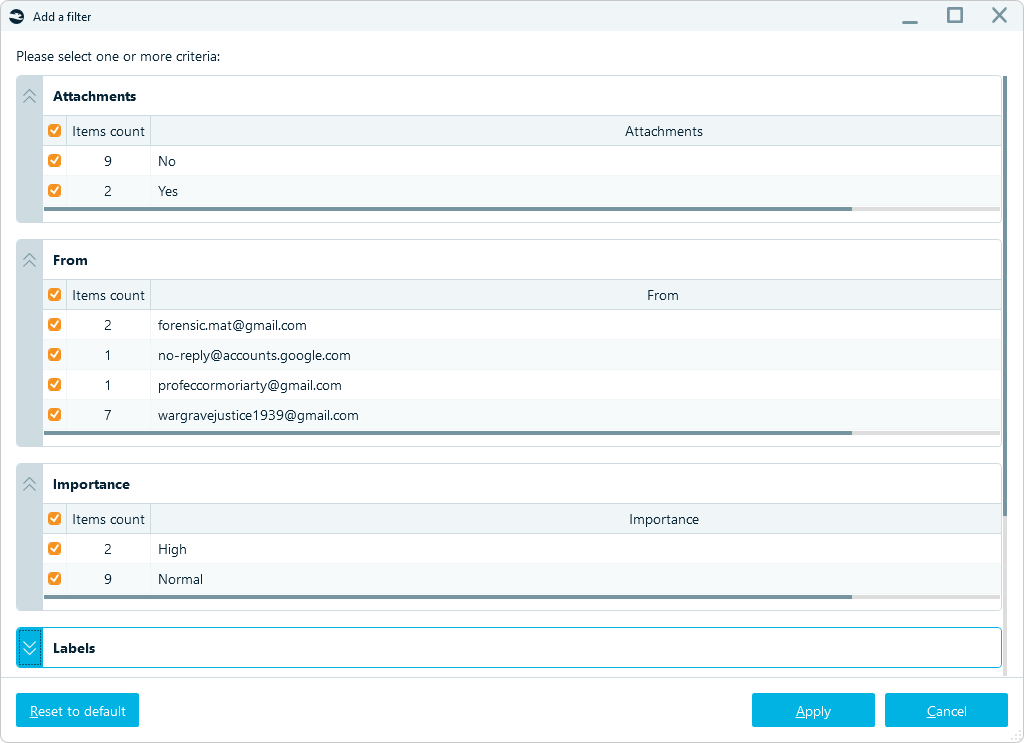
Email filtering options in Belkasoft X
Email content analysis
The content of emails may reveal signs of phishing, fraud, or malicious intent. Belkasoft X lets you preview email text content and run searches to identify suspicious keywords, links, or unusual language patterns. For instance, phishing emails may contain deceptive links or requests for sensitive information under the guise of urgency.
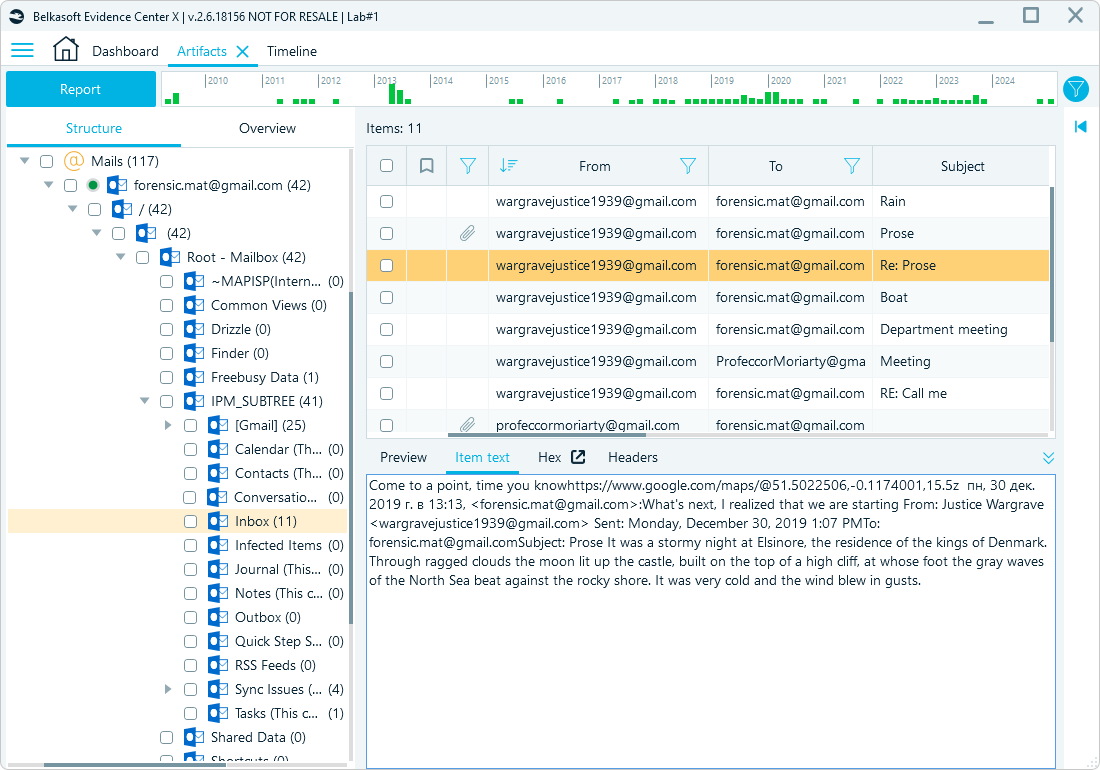
Email plain text preview in Belkasoft X
Email path analysis
To verify the authenticity of an email, you can analyze its routing path by examining the "Received" headers. These headers list the servers that handled the email, organized in reverse order, starting with the original server that received it.
You can cross-check IP addresses and routing servers against threat intelligence databases or manually verify them using WHOIS to identify whether servers belong to known malicious entities or operate in high-risk geolocations.
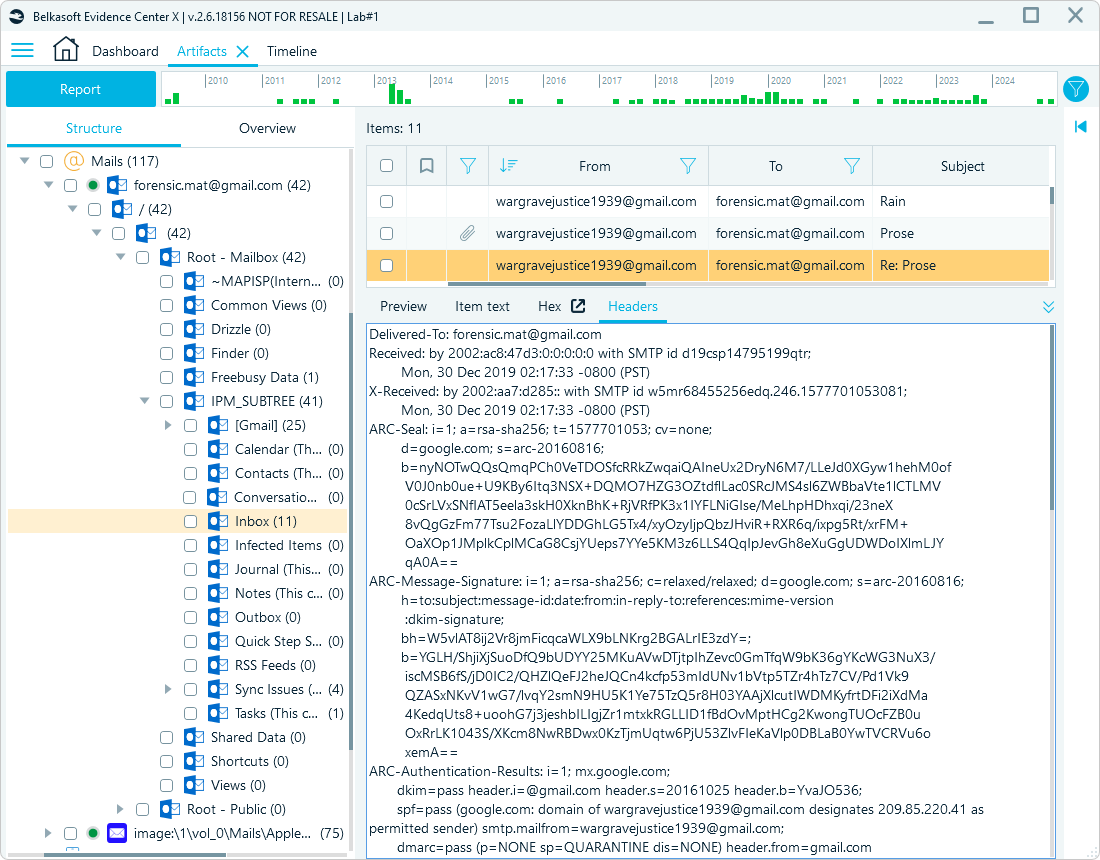
Email header view in Belkasoft X
Email tampering detection
Examining Authenticated Received Chain (ARC) records in email headers can identify potential email tampering. ARC provides a detailed chain of custody for the email as it passes through each server, including key elements like the ARC-Seal, ARC-Message-Signature, and ARC-Authentication-Results.
ARC is not required for basic email authentication and is implemented by intermediary servers (e.g., forwarding services, mailing lists) to preserve the original sender's authentication results (SPF/DKIM/DMARC) even after the email has been modified during forwarding. The absence of ARC records indicates that the email was sent directly, that intermediary servers do not support ARC (a rare case nowadays), or may signal an untrusted sender or tampering.
These authentication records summarize the results:
- DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) verifies email authenticity.
- SPF (Sender Policy Framework) validates that the sender is authorized.
- DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) validates domain-specific email policies.
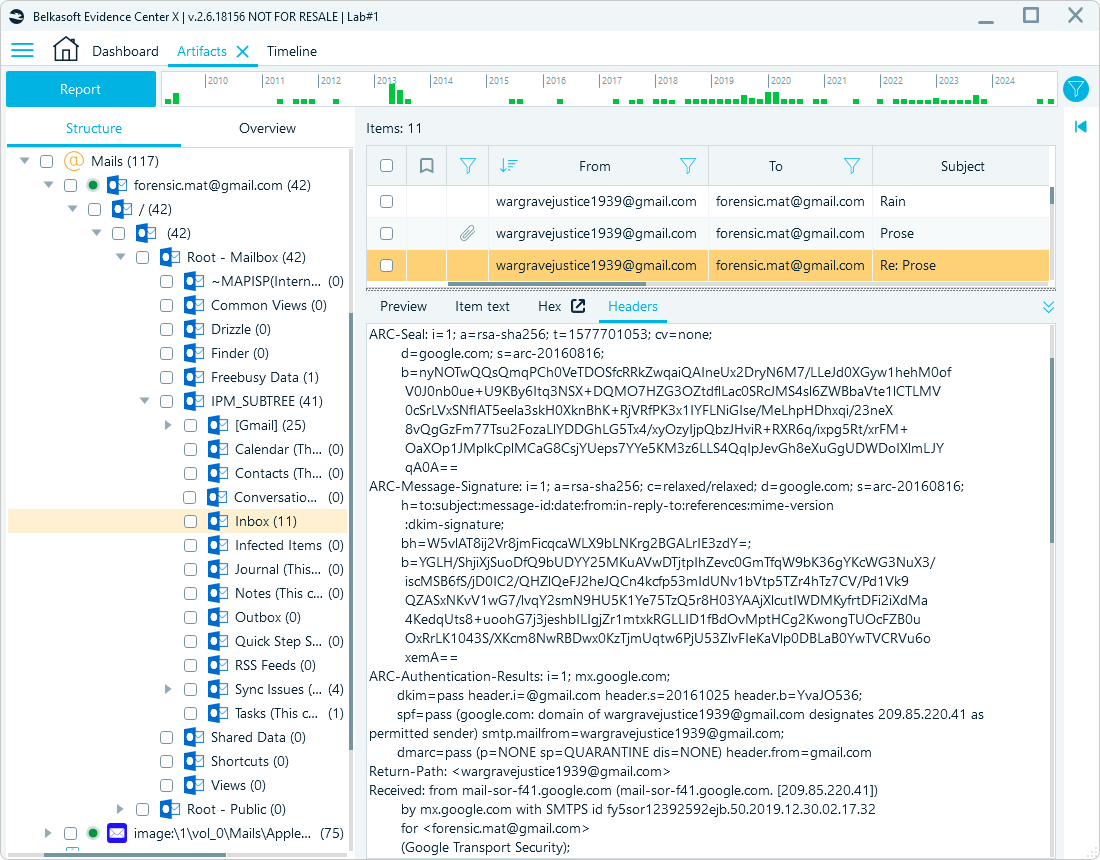
ARC-Seal records review in Belkasoft X
You can spot issues such as mismatched signatures, missing ARC records, or failed authentication results (for example, "dkim=fail"), indicating tampering or unauthorized access to an email.
Attachment analysis
Email attachments typically include various files, such as documents and images. In some cases, malicious actors may use attachments, for example, LNK files, to introduce malware into the recipient’s system.
Belkasoft X processes attachments similarly to embedded media in the documents, applying analysis methods that are appropriate for their formats.
To ensure all attachments from supported email formats are fully processed, enable the Analyze carved and embedded data option when adding a data source:
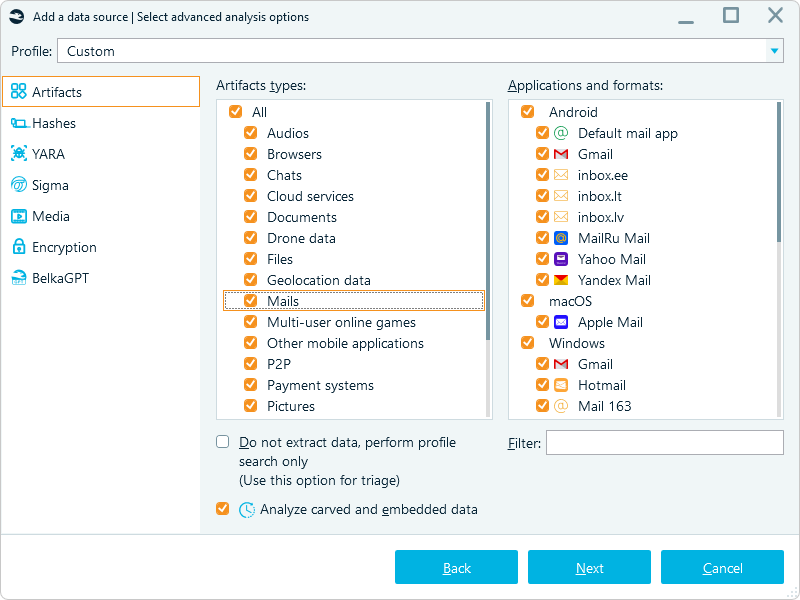
Enabling carved and embedded data analysis in Belkasoft X
Without this option enabled, Belkasoft X will still extract attachments and display them under relevant artifact categories (such as Pictures or Documents). However, enabling it allows Belkasoft X to extract metadata (if any) from attachments and apply additional analysis options, such as text recognition and picture classification:
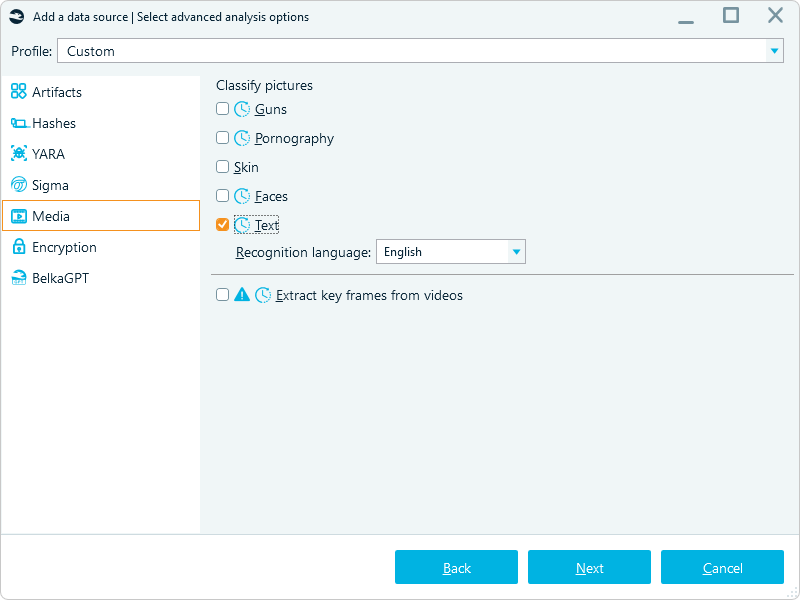
Enabling media analysis and classification options in Belkasoft X
If you need to analyze email attachments as files, you can export all attachments from the required email folder node:
Copy attachments to the folder menu option
When copying attachments, Belkasoft X preserves the original structure of the email folders they belong to:
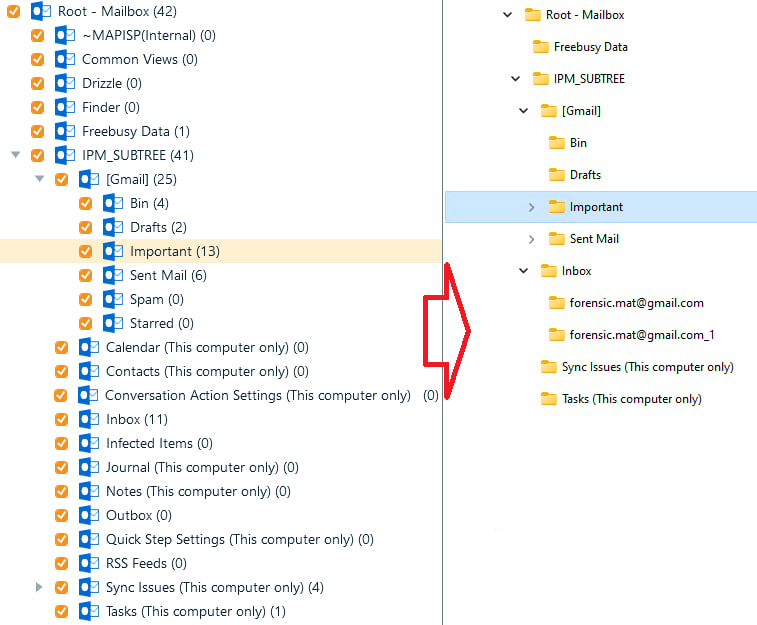
Exported data
You can subsequently reimport attachments to Belkasoft X to process them with YARA rules or hashset analysis or analyze them with other tools. The structure will help you track file origins. For example, if a tool detects malware embedded in a file, you will be able to quickly figure out whether it was located in the Inbox or the Spam folder.
Email data analysis techniques
Email investigations often involve sifting through vast amounts of data, with a single case potentially containing thousands of emails and related artifacts. Belkasoft X offers several techniques to help:
- Use global filters: Refine all artifacts available in the case by date ranges or specific keywords. This technique helps identify connections between email data and other artifact types available in the data source.
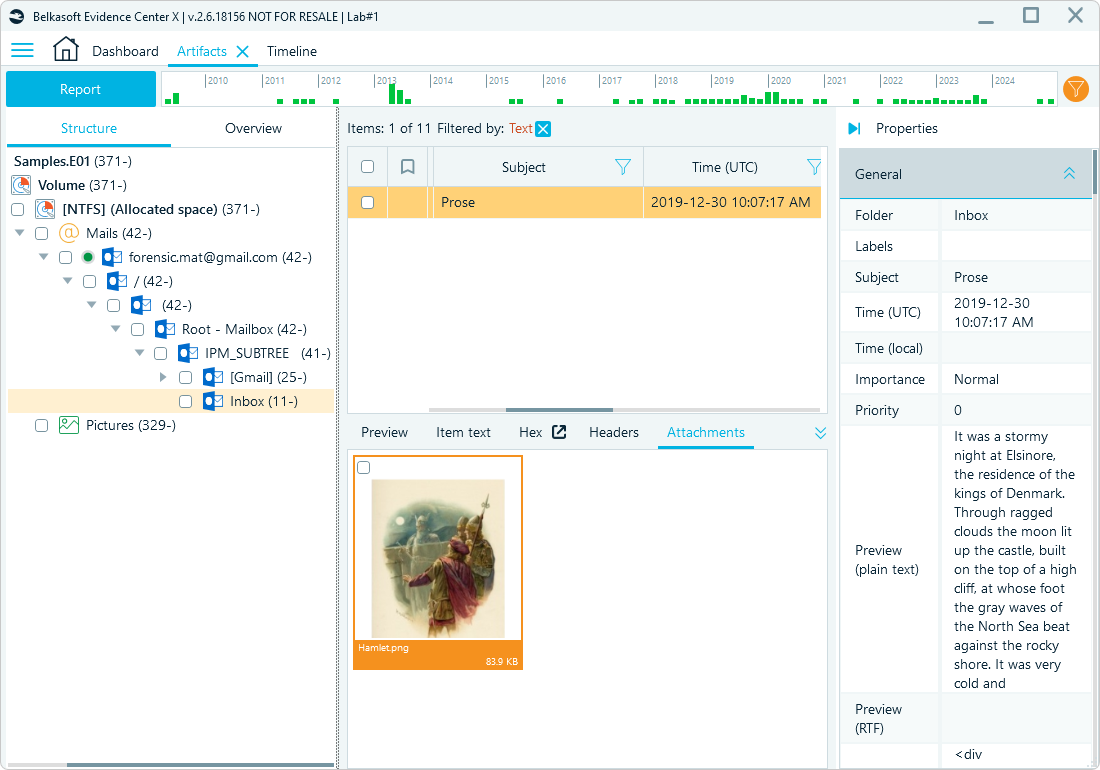
Case data filtered by the word "hamlet"
- Focus on timelines: Align email activity with other events within specific time frames in the Timeline window, or apply the Mails category filter to focus on emails.
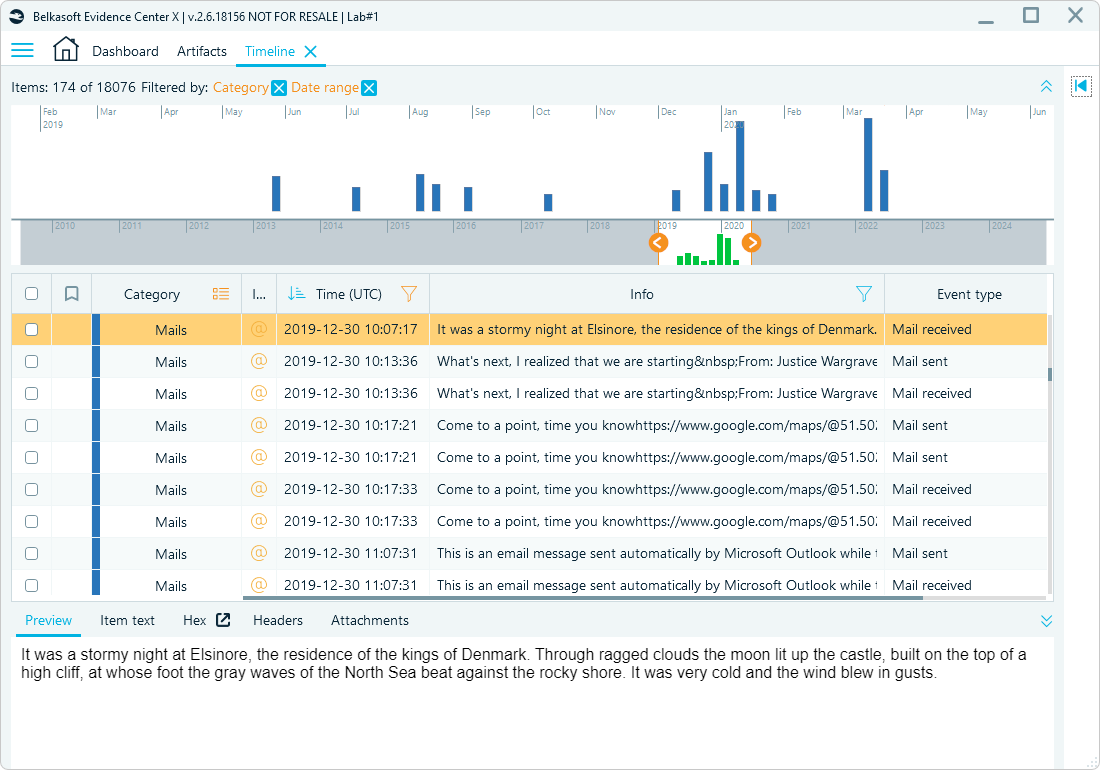
Timeline view in Belkasoft X
- Visualize communication with the Connection Graph: Map email correspondence and account interactions to reveal communication patterns and relationships.
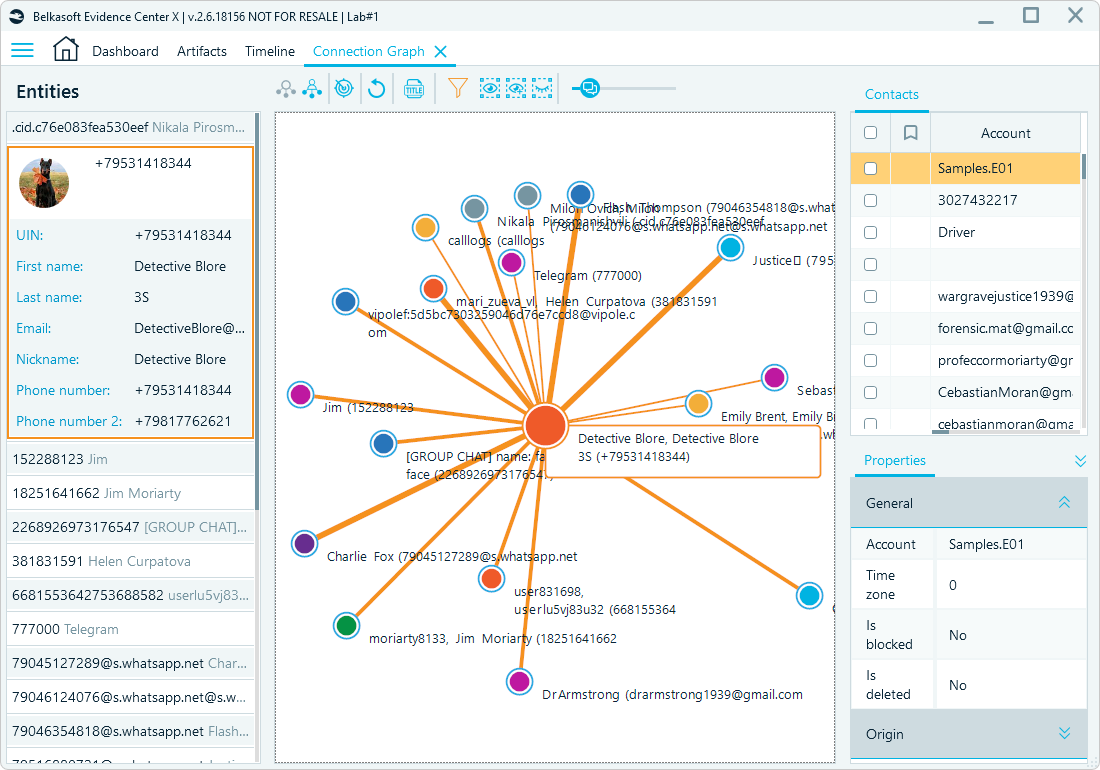
Connection graph in Belkasoft X
- Automate attachment analysis: Review the attached media using image classification and text extraction options.
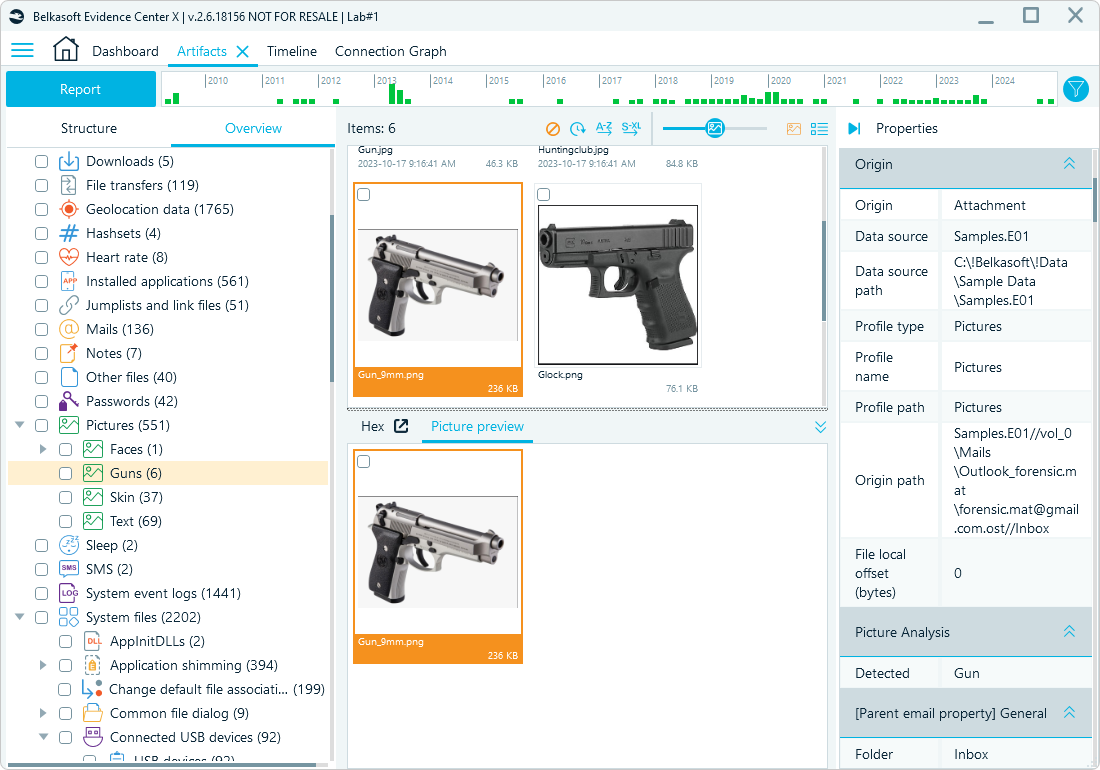
Email attachments categorized in Belkasoft X
Reporting on and exporting email evidence
In the different stages of your investigation, Belkasoft X allows you to create reports in various formats. You can report on email findings using standard formats like CSV or PDF, or you can export them as EML files to share with peers and for further processing.
By default, all EML files are saved to the same output folder, but if you need a more structured output, you can change the settings in Advanced options to create subfolders following the case tree:
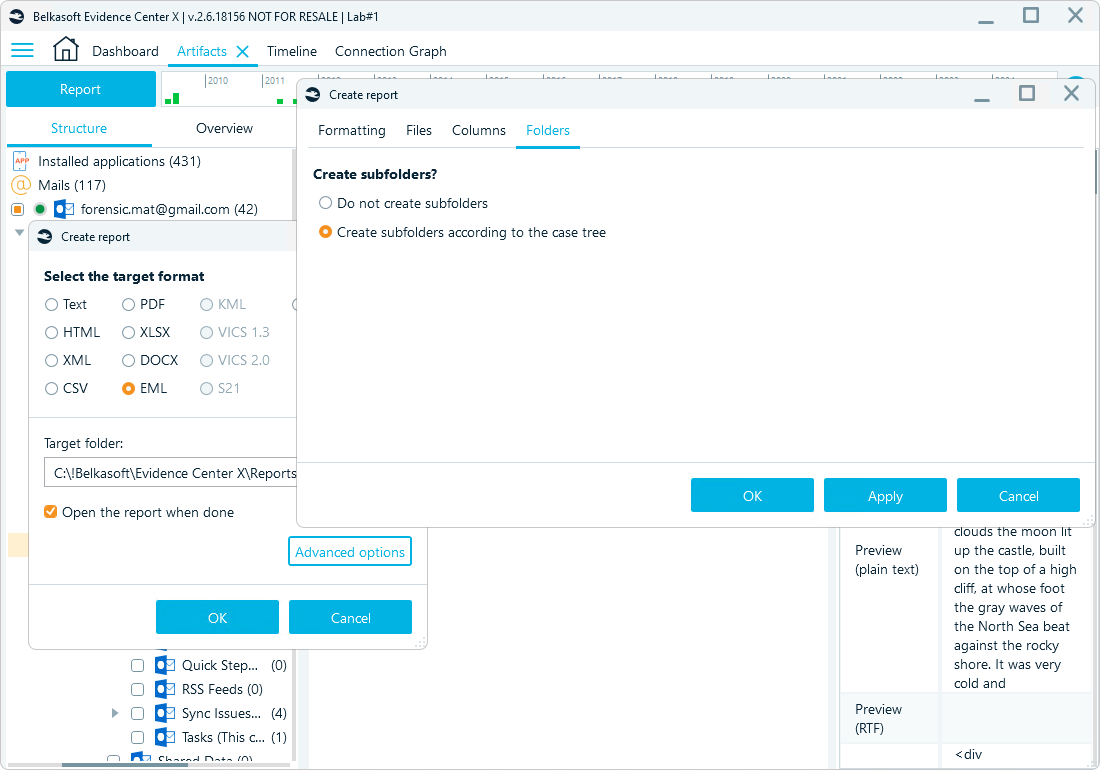
Report options in Belkasoft X
Exported emails will be split by email profile:
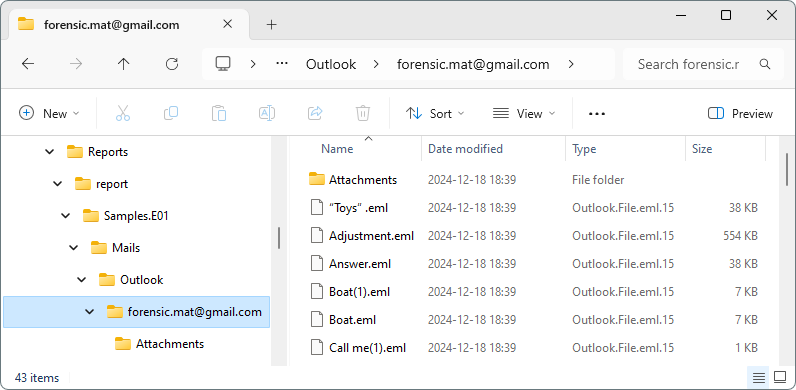
Belkasoft X output for emails
The option to copy attachments to the target folder is enabled by default for the EML format. The tool places all attachment files in a separate folder. If any of these files have the same names, Belkasoft X renames them by adding a number postfix, such as _1, _2, and so on:
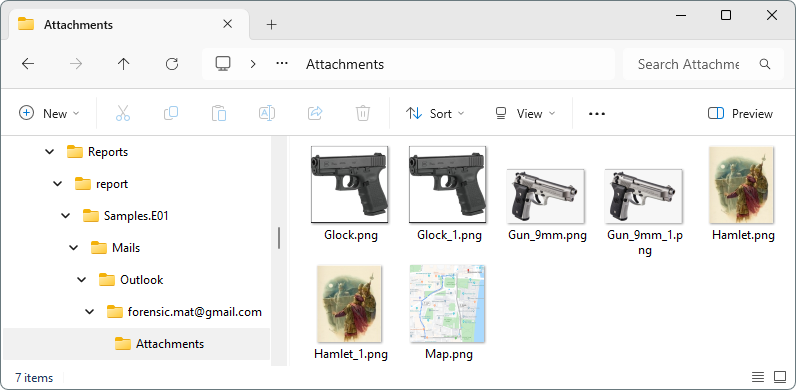
Belkasoft X output for email attachments
If you do not want to export attachments along with EMLs, you need to change the settings in advanced report options. Go to the Files tab and clear the Copy embedded files or attachments into the target folder checkbox.
The additional "cherry on top" for exported emails and attachments is the ability to run your extracted data through YARA rules or hashset analysis.
Conclusion
Mailbox forensics plays a vital role in uncovering critical evidence within email communications, whether it involves identifying phishing attempts, tracing malware delivery, or analyzing user interactions. Belkasoft X enhances this process by offering robust tools for analyzing metadata, content, attachments, and connections.
Features like YARA rule integration and the Connection Graph streamline investigations, allowing you to handle large datasets and uncover meaningful insights efficiently. By leveraging these capabilities, you can extract and present actionable intelligence from mailbox data faster and more precisely.

